The healthcare industry is undergoing a rapid change. Thanks to technological advancements, doctors can now diagnose patients without ever seeing a patient face to face. From algorithms that can predict a patient’s prognosis to remote monitoring solutions and robots that perform can surgeries, technology impact is in all areas of healthcare.
When we think of the latest trends in technology, Blockchain, AI and IoT come to mind. The backbone of all these technological trends is cloud computing. Cloud computing makes innovations like AI-powered chatbots and IoT based healthcare applications possible. The digitization of healthcare data has paved the way for massive shifts in the consumption, storage, and sharing of medical data.
In this article, let’s take a look at the types of cloud computing and the benefits of cloud computing in healthcare. But first, let’s cover the basics.
Overview
- What is Cloud Computing in Healthcare?
- Types of Cloud Computing in Healthcare
- Benefits of Cloud Computing in Healthcare
- Risks of Cloud Computing in Healthcare
- Final Thoughts
What is Cloud Computing in Healthcare?
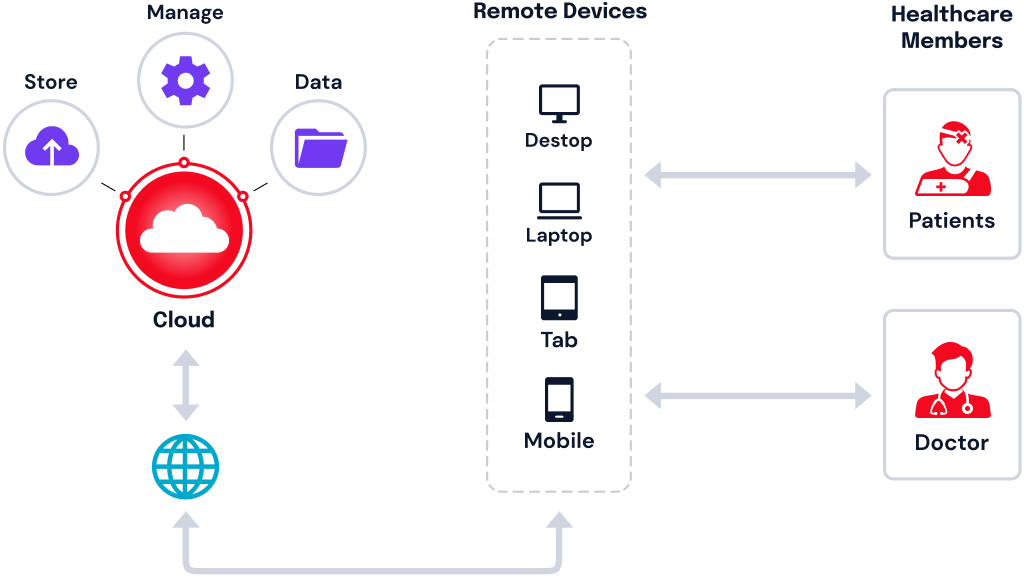
From Netflix to Gmail and online banking, we use a bunch of cloud computing solutions everyday without even realizing it.
Cloud computing in the healthcare industry is the concept of leveraging the power of the internet to store, manage, and process healthcare data from a remote server. In contrast to traditional data centers, cloud computing is inexpensive, scalable and supports collaboration.
It gives patients access to their Electronic Medical Records (EMR) and also enables them to receive on-demand remote consultation. From a healthcare provider’s standpoint, cloud computing breaks down location barriers.
Types of Cloud Computing in Healthcare
Cloud computing allows customers to leverage a cloud providers’ infrastructure, platforms, and software in a flexible and cost-efficient manner . There are two models of cloud computing in healthcare – distribution and deployment models. Software as a Service (SaaS), Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS), and Platform as a Service (PasS) are all options of deploying the distribution model . Private, Community, Public, and Hybrid deployment models are all options of deployment cloud computing models.
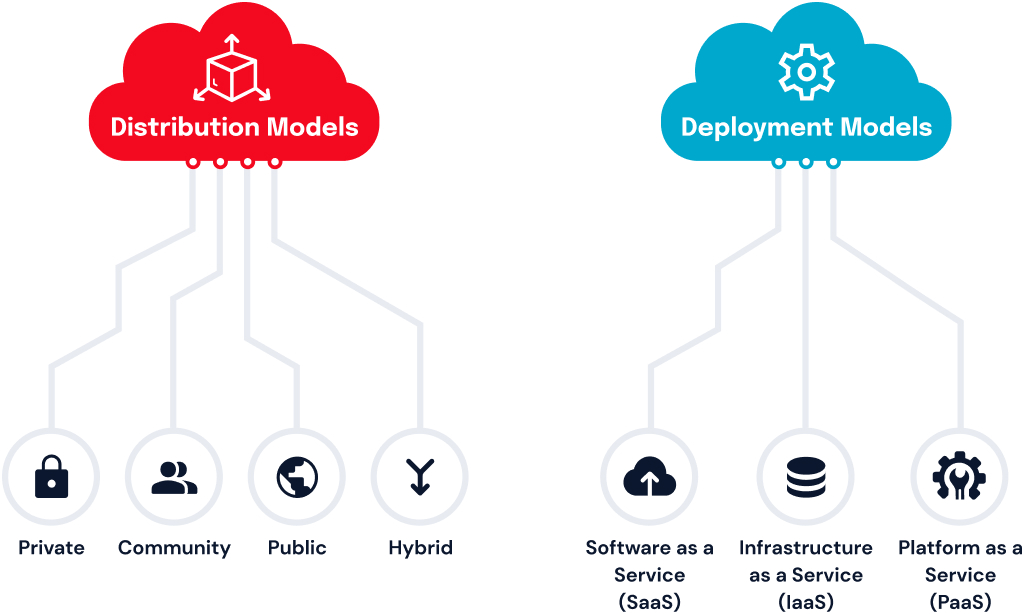
Cloud Computing by Deployment Model
- Private – The cloud network is private. Only the healthcare group/hospital can use the cloud facility.
- Community – The cloud network is shared by a group of healthcare bodies.
- Public – The cloud is open. All the stakeholders have access to the network. This aids in faster sharing of knowledge in the medical field.
- Hybrid – This model is a combination of some elements of all the other deployment models.
Cloud Computing by Distribution Model
- Software as a Service (SaaS) – In this cloud computing distribution model, a cloud provider hosts the healthcare applications and makes them available to clients.
- Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS) – The cloud provider sets up the IT infrastructure, operating system in this case for the client to deploy applications.
- Platform as a Service (PaaS) – The cloud provider distributes a ready-to-use platform for the client. The IT infrastructure, operating system, applications, and other components are distributed and the client can set up the environment quickly.
Benefits of Cloud Computing in Healthcare
In short, cloud computing supports healthcare technologies such as electronic medical records, patient portals and innovations such as IoT healthcare devices, and big data analytics.Let’s take a look at how cloud computing can benefit the healthcare industry.
Cost-Effective Healthcare Data Storage
Maintaining patient data is a cumbersome task. Especially in this era where data needs to be collected and stored from various sources, such as EMRs, prescriptions, insurance claims, healthcare app data, and wearables. Cloud computing allows hospitals to pay as they go for IT infrastructure. Hospitals and healthcare providers no longer need to purchase expensive data storage hardware and software or manage the infrastructure on their own. This helps hospitals to grow faster and offer better service.
Telemedicine
Ever since the pandemic, telemedicine has gained popularity. Cloud-based applications and telehealth systems allow patients to reach out to the healthcare professionals without location or time constraints. From video conferencing medical sessions to even tracking consumption of medicines, telemedicine has become an integral part of healthcare. In a nutshell, cloud computing is the key to better telemedicine.
Improved Patient Experience
Healthcare groups and clinicians can now provide a patient with real-time access to lab test results, medical information, and even doctor’s notes, thanks to cloud computing. Patients have the flexibility to share their medical records and get a second opinion with another clinician in a short span of time. Documented health records on cloud prevents patients from being overprescribed or dragged into unneeded testing. Medical data can be archived and retrieved easily when stored on the cloud.
Enhanced Collaboration
Cloud computing in healthcare plays a major role in boosting collaboration. Patients no longer need to carry medical records while visiting a doctor. Doctors can share a patient’s history with other specialists, check earlier consultations with other healthcare professionals as well. Cloud computing facilitates collaboration which in turn enables doctors to provide a more accurate treatment.
Risks of Cloud Computing in Healthcare
Despite all the benefits that healthcare cloud computing offers, there are still some risks.
Implementation Risks
Switching from an on-premises installation to the cloud is a specialist task. Clinicians or healthcare groups would need to locate experienced developers and cloud experts who can integrate new technology without glitches. Otherwise, your company may experience outages, poor data processing, or information leaks. Next, there is a learning curve, hospitals need to train their staff on how to work productively in the cloud.
Security risks
Storing medical data in the cloud comes with a risk of attack. While cloud networks provide security tools to monitor the environment for threats and deal with threats, it is not foolproof. Currently in the US alone, there are over 500 cases cases of security breaches leading to a hack of the patient’s health information. Hospitals need to invest in a team that could monitor and tackle attacks such as DDoS effectively.
Regulatory Compliance
Patient data is one of the most sensitive held by healthcare providers. It is protected by regularities such as HIPAA and the GDPR. Healthcare providers have a legal obligation to protect patients’ data and to notify them of data breaches as part of these legislation’ duties. Failing to protect confidential patient data can result in a hefty charge. To ensure that patient data is protected, security mechanisms such as access controls, authentication, and storage security must be implemented. This is one reason why most healthcare providers are reluctant to make the shift to the cloud.
Storage reliability
Selecting a cloud service provider who is capable of supporting your workload is the key to avoiding unnecessary downtime. Most cloud providers offer the flexibility to pay on the go. If your usage requirements surpasses your current cloud computing strategy, you may face some issues accessing data on-demand or face performance difficulties such as latency. It is very important to choose a trusted cloud service provider for improved security and reduced chance of unplanned downtime.
Final Thoughts
While moving to the cloud carries some significant risks, it also presents a wonderful potential for healthcare organizations to improve patient care. All of the risks can be mitigated by completing thorough study and determining what security measures are required to safeguard data stored in the cloud. Part of it is understanding your cloud provider’s duties, as well as your own, so you don’t expose your firm to legal or financial danger.
At SolutionChamps, we have years of experience in digital transformation and implementing IoT based healthcare solutions. Discuss your project idea and get an attractive quote today!